Topic
Marine Technology
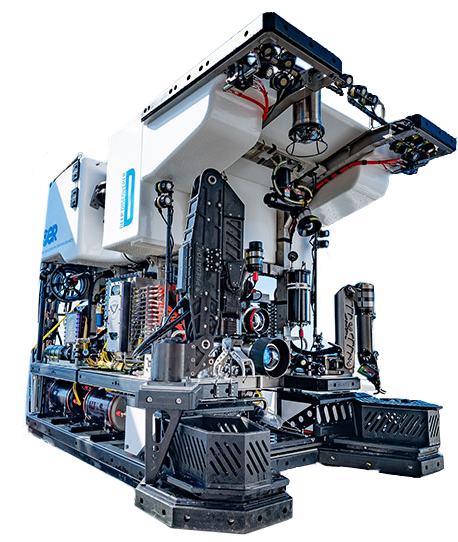
What is an ROV?
ROV stands for Remotely Operated Vehicle. ROVs are tethered to and operated from a ship allowing humans to explore the ocean without actually being in the vehicle.
Lights
High power LEDs bring light to the dark depths of the ocean so that cameras can capture exceptional images and video of the deep ocean world.
Sample Baskets
Containers that store biological specimens and geological samples to be brought to scientists for further study.
Manipulator Arm
What is an ROV?
Multi-joint arm with interchangeable jaws collect biological, geological, or archeological samples.
Cameras
Multiple cameras are mounted at different angles to take photos and high-definition video of the seafloor and water column to transmit back to explorers.
Customizable
Additional sensors can be added to the ROV to measure parameters like temperature, salinity, chemical compounds, and pressure.
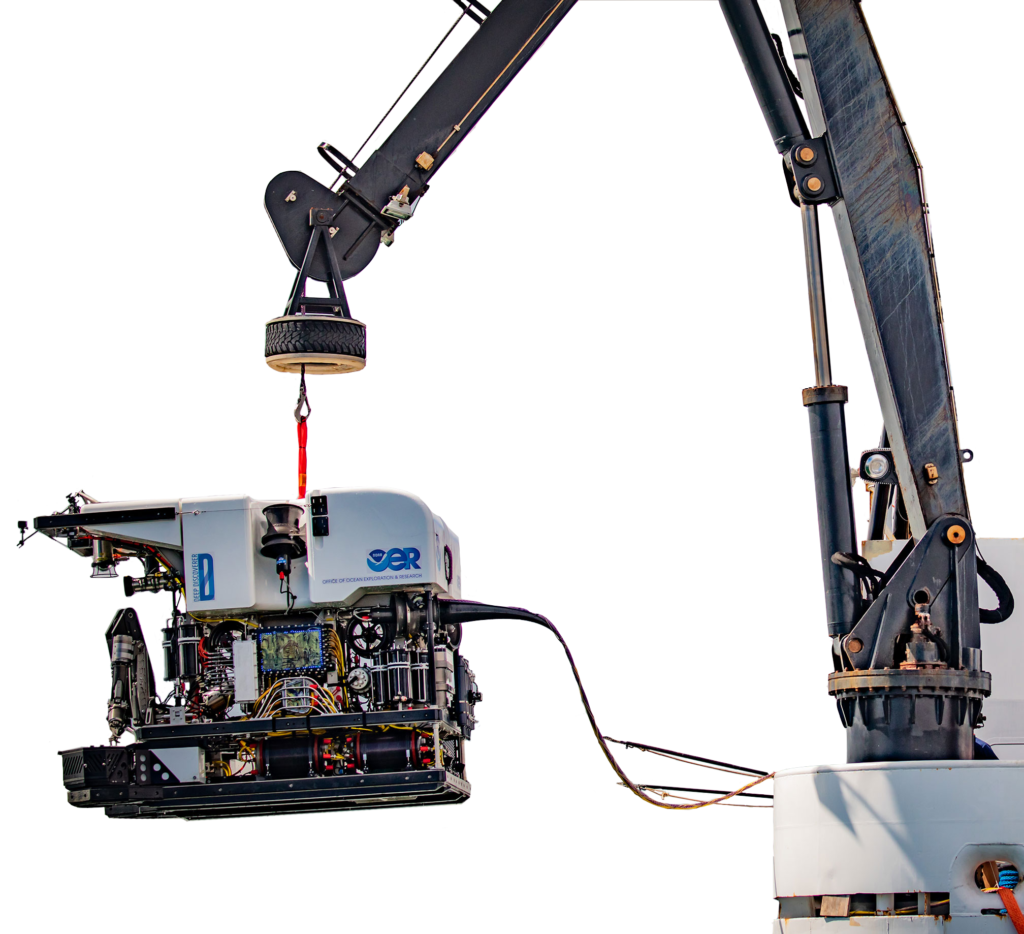
DAVIT
Small crane that stabilizes the ROV while it is being lowered into the water or retrieved after a dive.
Syntactic Foam
Supports the weight of the ROV and helps maintain neutral buoyancy in the water column.
Tether
Bundle of cables connecting the ROV to the ship that provides electricity to run cameras, lights, samplers, and sensors on the ROV and connectivity through fiber optics to send data to the ship at the surface.
Thrusters
Control the motion of the ROV underwater.
Control Room
Aboard the surface vessel pilots, engineers, and navigators work together to control the ROV.
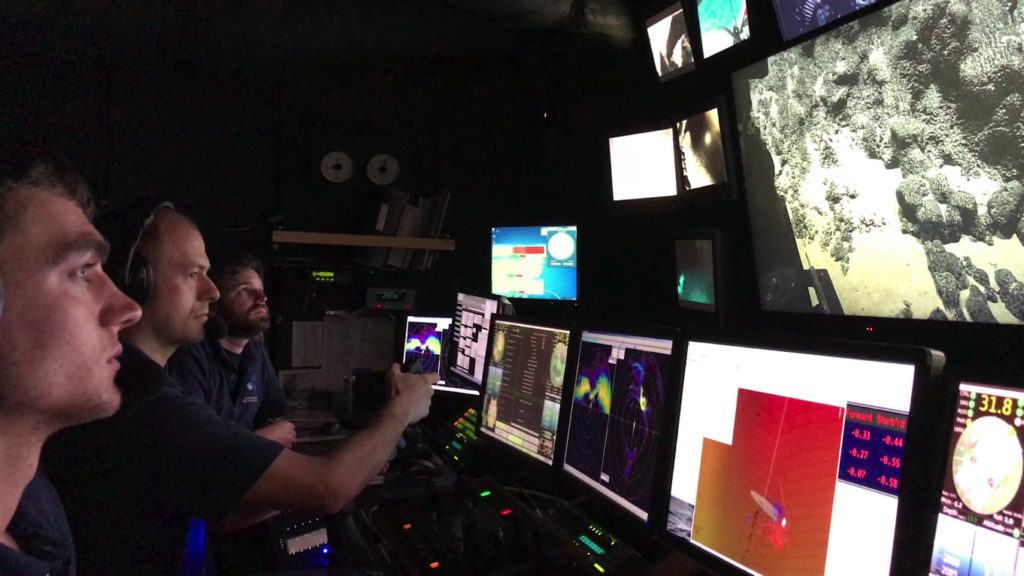
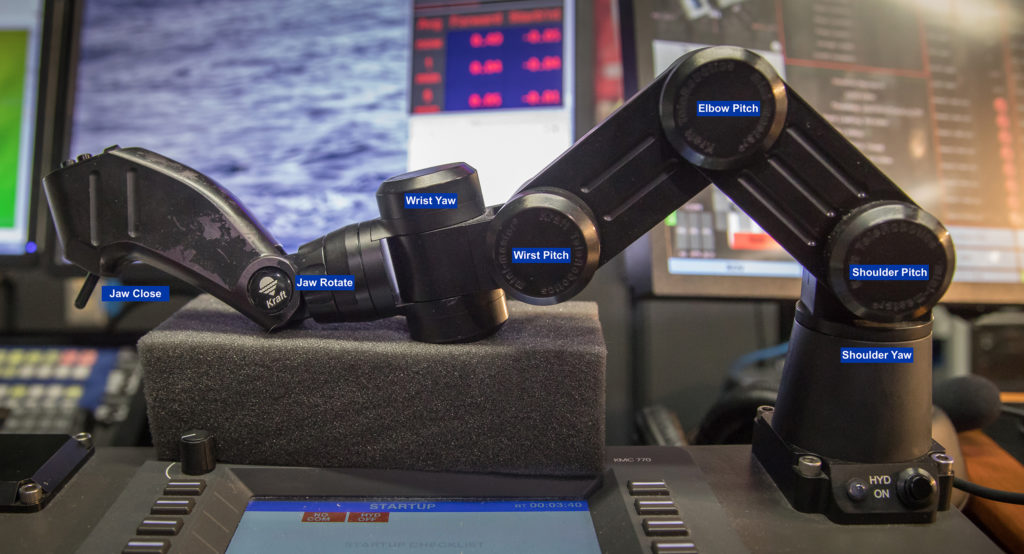


Laning, GFOE.
ROV Fun Facts
SMALLEST SCIENCE ROV: about the size of a large laptop BIGGEST SCIENCE ROV: about the size of a small truck
DEEPEST DIVE: ROVs can be designed for a variety of ocean depths and a few can descend to the deepest part of the ocean (~11,000 meters or ~36,200 feet)
LONGEST DIVE: several days