Topic
Hydrothermal Vents

Unique Vent Ecosystems
 By Dr. Diva Amon, Deep-Sea Biologist and Scientific Associate, Natural History Museum, London, UK; and
By Dr. Diva Amon, Deep-Sea Biologist and Scientific Associate, Natural History Museum, London, UK; and
 Dr. Deborah Glickson, Acting Board Director, National Academy of Sciences
Dr. Deborah Glickson, Acting Board Director, National Academy of Sciences
When most people think of the deep sea around the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) and the Marianas Trench Marine National Monument (MTMNM), they immediately think “the deepest part of the ocean.” And while the Mariana Trench is amazingly cool, there are other equally awesome habitats within the monument, such as hydrothermal vents.
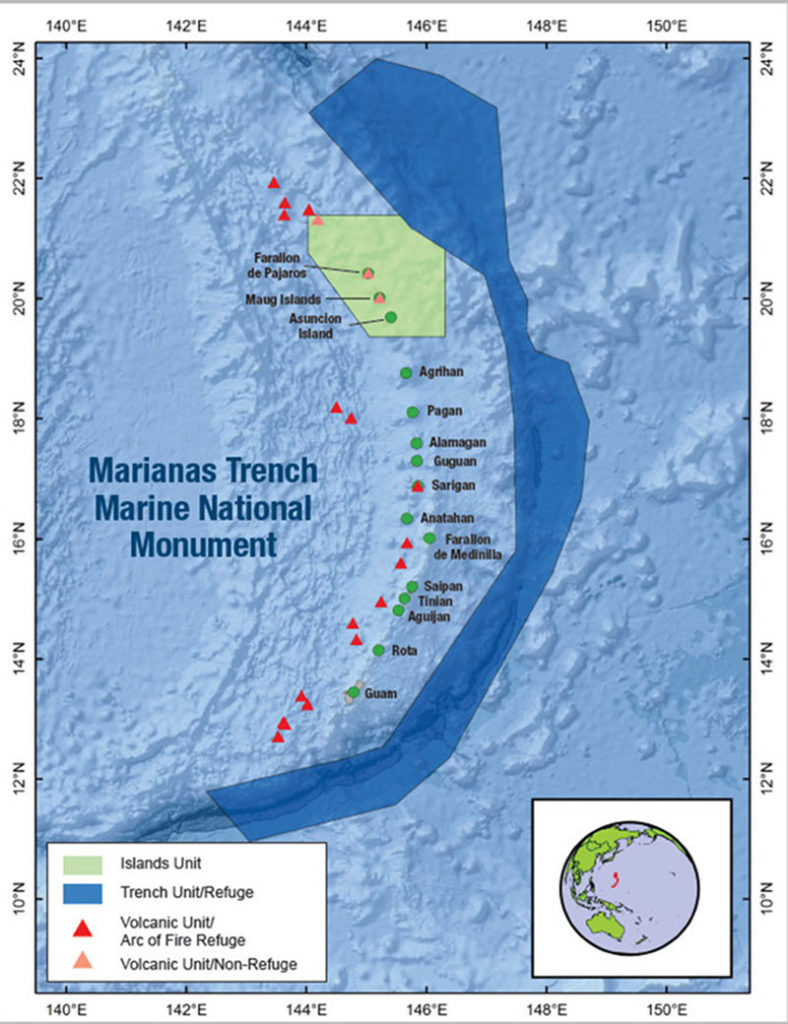
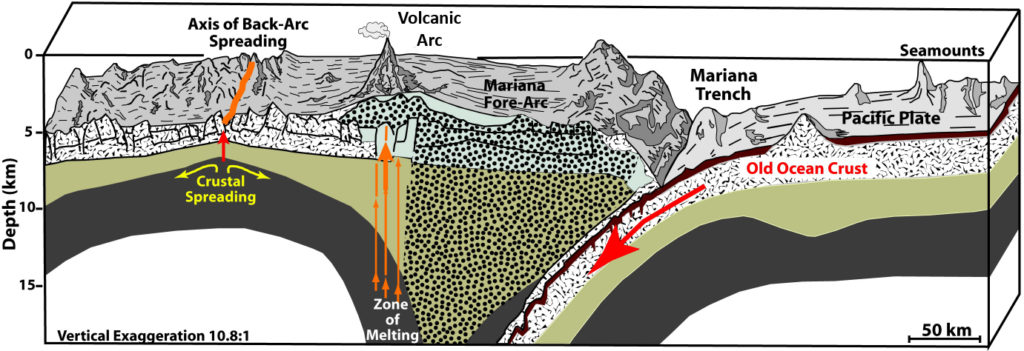
The Mariana Trench is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a tectonically active region where plates are colliding with each other, causing subduction (where one plate dives beneath another) or transform faulting (where plates slide by one another). The old seafloor of the Pacific Plate is subducting beneath the eastern part of the Mariana Plate, causing the mantle to melt and magma to rise, feeding the active volcanoes of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana volcanic arc system.
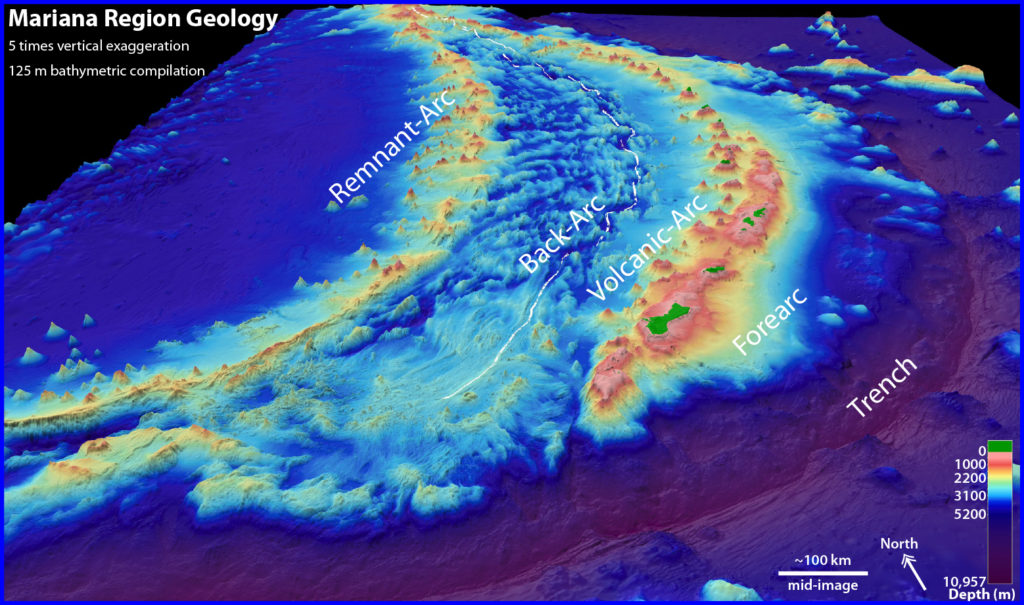
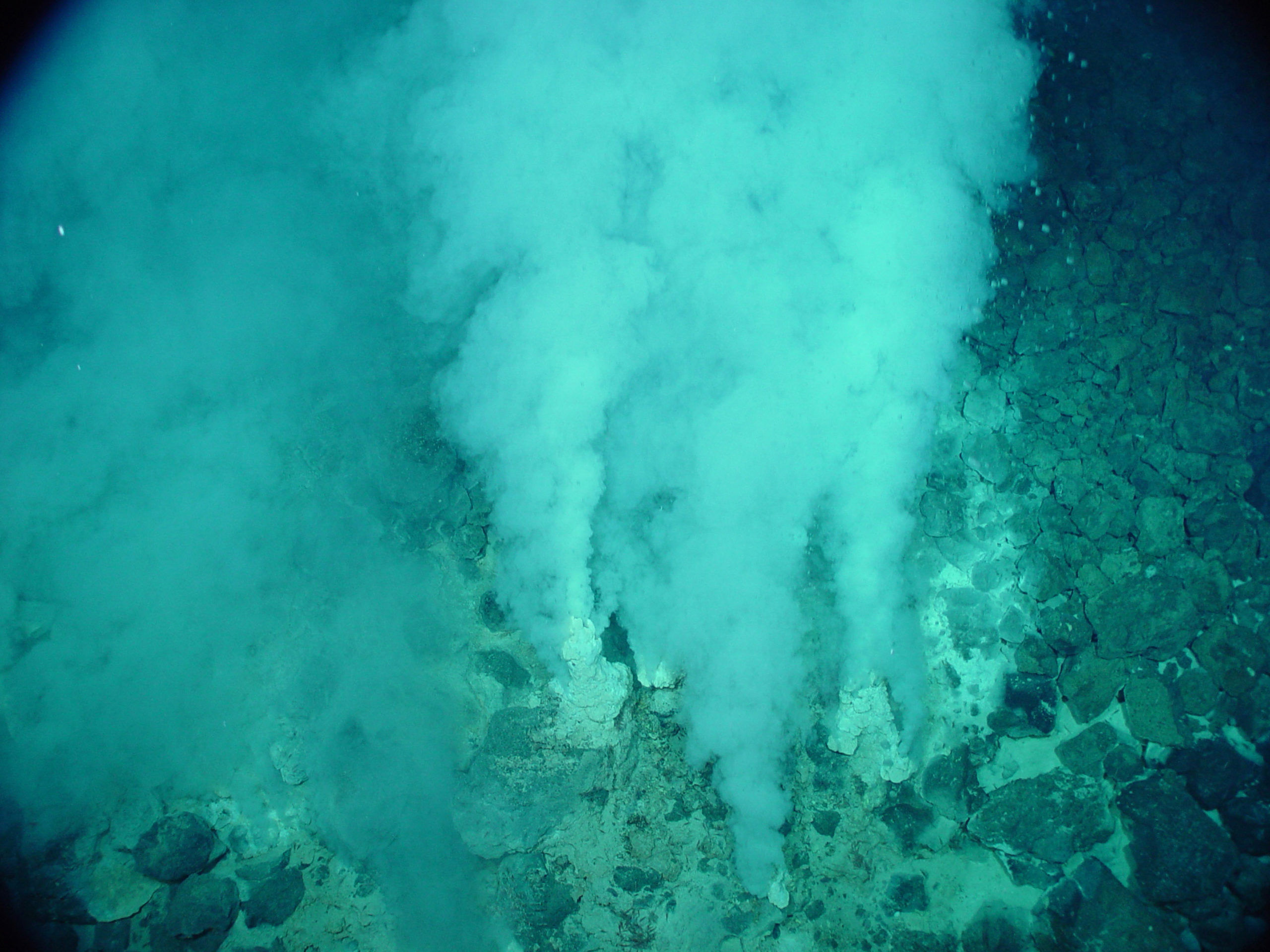
West of the arc volcanoes is the back-arc, a zone of extensional tectonics that causes spreading in the overriding plate and forms new oceanic crust. As seawater percolates downward through the oceanic crust, it becomes superheated and chemical-rich, eventually getting so buoyant that it comes back out at the seafloor surface. When the super-hot vent fluid meets the very cold water (2°C/35.6°F) of the deep sea, minerals that are carried in the fluid precipitate out of solution, forming spectacular vent chimneys. This chemical-rich vent fluid is also the source of life for much of the vent biota.
Chemoautotrophic bacteria use chemicals such as sulfides and methane as a source of energy to produce organic material. The process, called chemosynthesis, occurs in a similar way to which plants use sunlight to produce food via photosynthesis. Chemosynthetic bacteria are then grazed on by heterotrophs, which in turn are eaten by larger predators. Some of these bacteria even live inside vent fauna (such as tubeworms and Bathymodiolus mussels) or grow on specialized appendages (such as those seen on vent shrimp and Kiwa crabs).
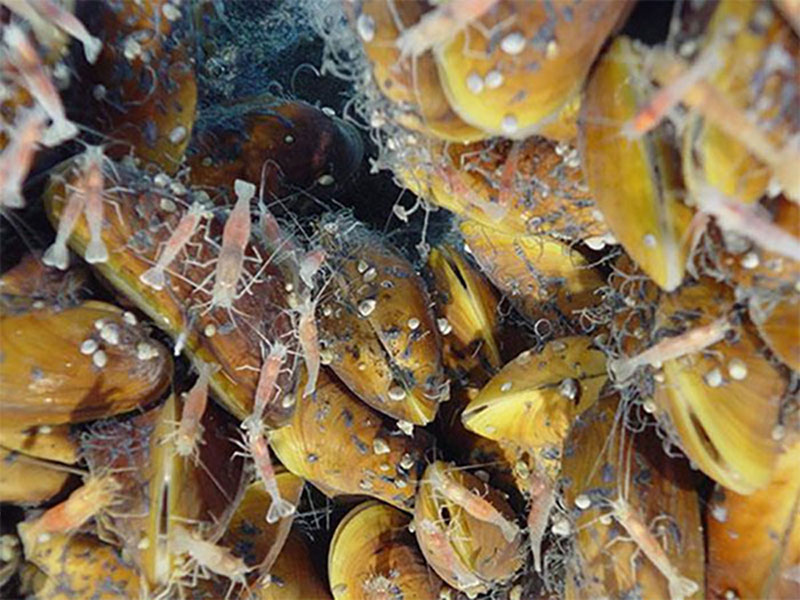

As food is plentiful and easy to obtain at hydrothermal vents, these sites are often oases of life in the deep sea. Animals are present in very high abundances, but there tends to be lower diversity, with communities being dominated by only a few types of organisms. Vent fauna tend to be similar regionally, but not globally, much like how similar animals are found on one continent but not between continents. However, it is not unusual for us to find new species at the vent sites we explore.
While some vents in the CNMI and MTMNM have been visited previously, there is still much to be discovered. These vents are unique in their sheer diversity – there are black smokers filled with sulfide minerals, liquid carbon dioxide vents at the NW Eifuku volcano, and even craters erupting molten sulfur! The volcanic arc is known to host vent fields that support a broad range of organisms, including gastropods, mussels, tubeworms, squat lobsters and shrimp.
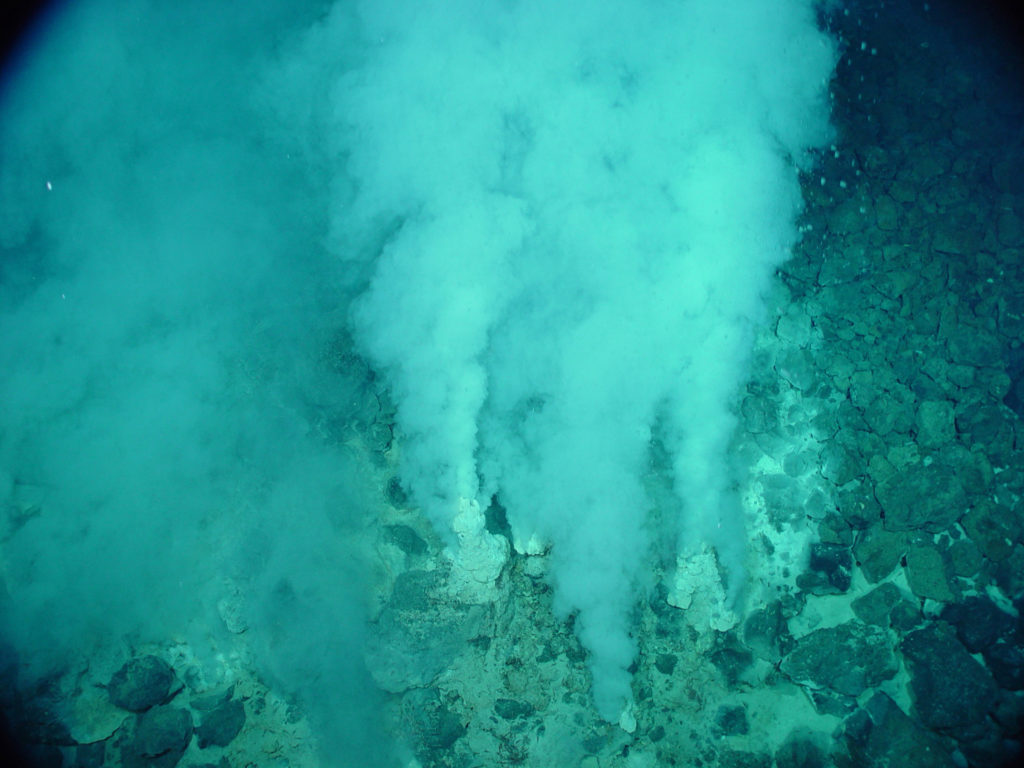

Exploring hydrothermal vents is so exciting because it teaches us about the limits of life – organisms living there have to deal with mind- boggling extremes of temperature and chemistry!